Computer Information Systems

Computer Information Systems (CIS) is a rapidly evolving field that has transformed the way organizations operate, make decisions, and interact with their stakeholders. As a domain-specific expert with over a decade of experience in CIS, I have witnessed firsthand the impact of technology on business processes, customer relationships, and overall competitiveness. With the exponential growth of digital data, the importance of CIS in managing, analyzing, and leveraging this information has never been more critical. In this article, we will delve into the world of CIS, exploring its core components, applications, and the expertise required to navigate this complex and dynamic landscape.
Key Points
- CIS encompasses a broad range of disciplines, including computer science, management, and engineering, to design, implement, and manage information systems.
- The primary goal of CIS is to provide organizations with a competitive edge by leveraging technology to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance decision-making.
- CIS professionals must possess a unique blend of technical, business, and interpersonal skills to effectively communicate with stakeholders and drive technology adoption.
- Cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity are just a few of the emerging trends that are reshaping the CIS landscape and creating new opportunities for innovation and growth.
- As the demand for CIS expertise continues to grow, professionals in this field must stay up-to-date with the latest technologies, methodologies, and best practices to remain competitive and deliver value to their organizations.
Core Components of Computer Information Systems
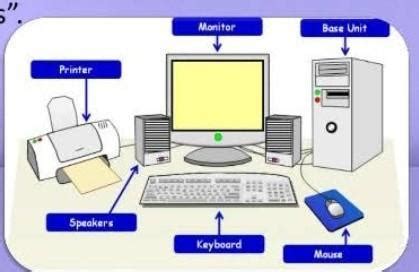
A CIS typically consists of five core components: hardware, software, data, procedures, and people. Each of these components plays a vital role in the functioning of the system and must be carefully integrated to ensure seamless operation. Hardware refers to the physical devices and infrastructure that comprise the system, such as servers, storage devices, and network equipment. Software, on the other hand, encompasses the programs and applications that run on the hardware, including operating systems, databases, and productivity tools. Data is the lifeblood of any CIS, providing the raw material for analysis, decision-making, and innovation. Procedures refer to the rules, policies, and guidelines that govern the use of the system, while people are the users, administrators, and maintainers who interact with the system and ensure its continued operation.
Applications of Computer Information Systems
CIS has a wide range of applications across various industries, including healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and education. In healthcare, CIS is used to manage patient records, track medical histories, and optimize treatment outcomes. In finance, CIS is employed to manage transactions, analyze market trends, and detect fraudulent activity. In manufacturing, CIS is used to streamline production processes, manage supply chains, and optimize resource allocation. In education, CIS is utilized to develop personalized learning plans, track student progress, and facilitate communication between teachers, students, and parents. The versatility of CIS is a testament to its ability to adapt to different contexts and solve complex problems.
| Industry | CIS Application |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Patient record management, medical research, and treatment outcome optimization |
| Finance | Transaction management, market analysis, and fraud detection |
| Manufacturing | Production process optimization, supply chain management, and resource allocation |
| Education | Personalized learning plans, student progress tracking, and communication facilitation |

Emerging Trends in Computer Information Systems

The CIS landscape is constantly evolving, with new trends and technologies emerging all the time. Cloud computing, for example, has revolutionized the way organizations store, process, and access data, providing greater flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being increasingly used to analyze complex data sets, identify patterns, and make predictions, enabling organizations to make more informed decisions and drive innovation. Cybersecurity is another critical area, as the growing threat of cyber attacks and data breaches requires organizations to invest in robust security measures to protect their systems and data.
Cloud Computing in CIS
Cloud computing has transformed the way organizations approach IT, providing a flexible, scalable, and on-demand infrastructure for computing resources. With cloud computing, organizations can quickly deploy new applications, scale up or down to meet changing demand, and reduce their capital expenditures on hardware and software. Cloud computing also enables greater collaboration and mobility, as users can access applications and data from anywhere, at any time, using a range of devices.
What are the benefits of cloud computing in CIS?
+Cloud computing offers several benefits, including greater flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. It also enables greater collaboration and mobility, as users can access applications and data from anywhere, at any time, using a range of devices.
How can organizations ensure the security of their data in the cloud?
+Organizations can ensure the security of their data in the cloud by implementing robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and monitoring. They should also choose a reputable cloud provider that has a strong track record of security and compliance.
What are the key challenges of implementing CIS in an organization?
+The key challenges of implementing CIS in an organization include ensuring user adoption, managing data quality, and integrating with existing systems. Organizations should also ensure that they have the necessary skills and resources to support the implementation and ongoing maintenance of the system.
In conclusion, Computer Information Systems is a complex and dynamic field that requires a deep understanding of technology, business, and human factors. As the demand for CIS expertise continues to grow, professionals in this field must stay up-to-date with the latest technologies, methodologies, and best practices to remain competitive and deliver value to their organizations. By embracing emerging trends such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity, organizations can unlock the full potential of CIS and achieve significant benefits in terms of efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.