Dense Irregular Tissue
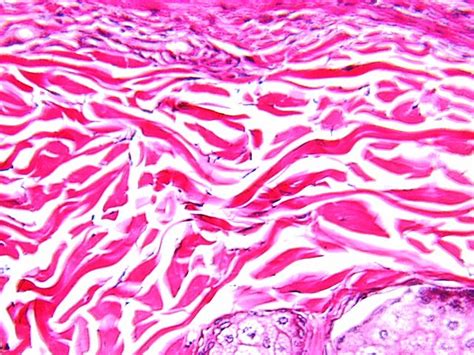
Dense irregular tissue, a type of connective tissue, plays a crucial role in the structural framework of various organs and systems within the human body. Characterized by its dense arrangement of collagen fibers and fibroblasts, this tissue type is uniquely adapted to provide strength, support, and elasticity to tissues that are subject to constant stress and tension. The irregular arrangement of fibers in this tissue allows it to withstand forces from multiple directions, making it an essential component of tissues such as the dermis of the skin, the capsules of organs, and the fasciae that surround muscles and other organs.
One of the key features of dense irregular tissue is its ability to resist deformation and maintain its shape under conditions of mechanical stress. This is primarily due to the high concentration of collagen fibers, which are the main structural proteins found in the extracellular matrix of connective tissue. Collagen fibers are secreted by fibroblasts, the primary cell type in connective tissue, and they provide the tissue with its strength and rigidity. The irregular arrangement of these fibers in dense irregular tissue allows it to distribute forces evenly across the tissue, thereby preventing damage and maintaining tissue integrity.
Key Points
- Dense irregular tissue is a type of connective tissue that provides strength, support, and elasticity to various organs and systems.
- It is characterized by a dense arrangement of collagen fibers and fibroblasts, with fibers arranged irregularly to withstand forces from multiple directions.
- The tissue plays a crucial role in the dermis of the skin, the capsules of organs, and the fasciae surrounding muscles and other organs.
- The high concentration of collagen fibers in dense irregular tissue allows it to resist deformation and maintain its shape under mechanical stress.
- Fibroblasts are the primary cell type in dense irregular tissue, responsible for secreting collagen fibers and maintaining tissue structure.
Structure and Function of Dense Irregular Tissue

The structure of dense irregular tissue is specialized to provide maximum strength and support to tissues that are subject to constant mechanical stress. The tissue is composed of a dense network of collagen fibers, elastin fibers, and fibroblasts, which are embedded in a ground substance that provides nutrients and allows for the exchange of waste products. The collagen fibers in dense irregular tissue are arranged in a random, irregular pattern, which allows the tissue to distribute forces evenly and resist deformation in multiple directions.
In terms of function, dense irregular tissue plays a critical role in maintaining the structural integrity of various organs and systems. For example, in the dermis of the skin, dense irregular tissue provides the necessary strength and elasticity to maintain skin integrity and allow for movement and flexion. Similarly, in the capsules of organs such as the liver and kidneys, dense irregular tissue provides a protective layer that helps to maintain organ shape and prevent damage from mechanical stress.
Role of Fibroblasts in Dense Irregular Tissue
Fibroblasts are the primary cell type in dense irregular tissue, and they play a crucial role in maintaining tissue structure and function. Fibroblasts are responsible for secreting collagen fibers and other components of the extracellular matrix, such as elastin and ground substance. They also play a key role in tissue repair and remodeling, by secreting enzymes that break down damaged tissue components and promoting the deposition of new collagen fibers and other matrix components.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Collagen fibers | Provide strength, rigidity, and elasticity to tissue |
| Fibroblasts | Secrete collagen fibers and other matrix components, maintain tissue structure and function |
| Elastin fibers | Provide elasticity to tissue, allow for movement and flexion |
| Ground substance | Provides nutrients and allows for exchange of waste products, maintains tissue hydration |

Clinical Significance of Dense Irregular Tissue
Dense irregular tissue plays a critical role in maintaining the structural integrity of various organs and systems, and alterations in tissue structure or function can have significant clinical implications. For example, changes in the composition or arrangement of collagen fibers in dense irregular tissue can lead to conditions such as fibrosis, where excessive collagen deposition can lead to tissue scarring and loss of function. Similarly, injuries to tissues that contain dense irregular tissue, such as the skin or fasciae, can lead to significant morbidity and mortality if not properly managed.
In addition to its role in maintaining tissue structure and function, dense irregular tissue also plays a critical role in the healing process. After injury, fibroblasts in dense irregular tissue are activated to secrete collagen fibers and other matrix components, which helps to repair damaged tissue and restore tissue function. However, excessive or inappropriate deposition of collagen fibers can lead to the formation of scar tissue, which can have significant clinical implications.
What is the primary function of dense irregular tissue?
+The primary function of dense irregular tissue is to provide strength, support, and elasticity to various organs and systems, allowing them to withstand mechanical stress and maintain their shape.
What is the role of fibroblasts in dense irregular tissue?
+Fibroblasts are the primary cell type in dense irregular tissue, and they play a crucial role in maintaining tissue structure and function by secreting collagen fibers and other matrix components.
What are the clinical implications of alterations in dense irregular tissue structure or function?
+Alterations in dense irregular tissue structure or function can have significant clinical implications, including the development of conditions such as fibrosis, tissue scarring, and loss of function.