Density Dependent Factors

Density dependent factors are a crucial aspect of understanding population dynamics and the intricate relationships within ecosystems. These factors refer to the influences that population density has on the birth and death rates of a species, ultimately affecting its overall population size. As the density of a population increases, the competition for resources such as food, water, and shelter intensifies, leading to a decrease in the population's growth rate. Conversely, when the population density is low, individuals have easier access to resources, resulting in an increase in the population's growth rate.
The study of density dependent factors is essential in ecology, as it helps scientists understand how populations interact with their environment and how they respond to changes in their ecosystem. For instance, the concept of carrying capacity, which is the maximum population size that an environment can sustain indefinitely, is closely related to density dependent factors. As a population approaches its carrying capacity, density dependent factors such as increased competition for resources and predation become more pronounced, eventually leading to a stabilization of the population size.
Key Points
- Density dependent factors influence population growth rates by affecting birth and death rates.
- Competition for resources is a primary density dependent factor that impacts population size.
- Carrying capacity is a critical concept in understanding the relationship between population density and environmental sustainability.
- Predation and disease are also significant density dependent factors that can regulate population sizes.
- Understanding density dependent factors is essential for developing effective conservation strategies and managing ecosystems.
Density Dependent Factors and Population Growth
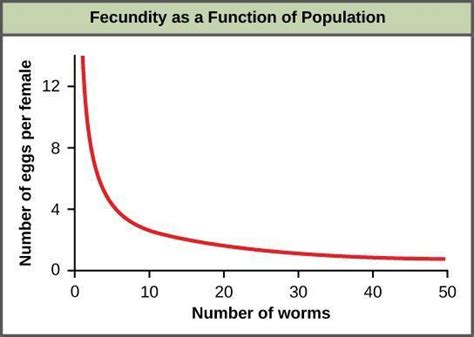
Density dependent factors play a crucial role in regulating population growth. As the population density increases, the competition for resources becomes more intense, leading to a decrease in the population’s growth rate. This is because individuals have to spend more energy competing for resources, which can lead to a decrease in reproductive success. Additionally, high population densities can also lead to an increase in disease transmission and predation, further reducing the population’s growth rate.
On the other hand, when the population density is low, individuals have easier access to resources, resulting in an increase in the population's growth rate. This is because individuals can allocate more energy to reproduction, leading to an increase in birth rates. Furthermore, low population densities can also reduce the transmission of diseases and the impact of predation, allowing the population to grow more rapidly.
Types of Density Dependent Factors
There are several types of density dependent factors that can impact population growth. These include:
- Competition for resources: As population density increases, competition for resources such as food, water, and shelter becomes more intense, leading to a decrease in the population's growth rate.
- Predation: High population densities can attract more predators, leading to an increase in mortality rates and a decrease in the population's growth rate.
- Disease: High population densities can facilitate the transmission of diseases, leading to an increase in mortality rates and a decrease in the population's growth rate.
- Environmental stress: High population densities can lead to environmental degradation, reducing the availability of resources and increasing the impact of environmental stressors such as pollution and climate change.
| Factor | Effect on Population Growth |
|---|---|
| Competition for resources | Negative |
| Predation | Negative |
| Disease | Negative |
| Environmental stress | Negative |

Case Studies: Density Dependent Factors in Action
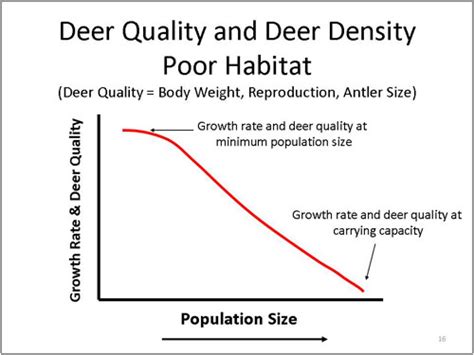
Several case studies demonstrate the impact of density dependent factors on population growth. For example, the introduction of rabbits to Australia in the 19th century led to a rapid increase in population size, resulting in overgrazing and environmental degradation. As the rabbit population density increased, competition for resources became more intense, leading to a decrease in the population’s growth rate. Eventually, the introduction of the myxoma virus, which targeted the rabbit population, further reduced the population size and alleviated the environmental pressures.
Another example is the dynamics of the African elephant population in national parks. As the elephant population density increases, competition for resources such as food and water becomes more intense, leading to a decrease in the population's growth rate. Additionally, high elephant population densities can also lead to environmental degradation, reducing the availability of resources and increasing the impact of environmental stressors such as drought and climate change.
Management and Conservation Implications
Understanding density dependent factors is essential for developing effective conservation strategies and managing ecosystems. By recognizing the impact of these factors, scientists and conservationists can work to mitigate the negative effects of high population densities and promote sustainable population growth. For example, conservation efforts can focus on reducing competition for resources by providing alternative food sources or improving habitat quality. Additionally, managing predation and disease transmission can also help to regulate population sizes and promote sustainable growth.
What are density dependent factors, and how do they impact population growth?
+Density dependent factors refer to the influences that population density has on the birth and death rates of a species, ultimately affecting its overall population size. These factors, such as competition for resources, predation, and disease, can regulate population growth by reducing the population’s growth rate as density increases.
How do conservation efforts address density dependent factors?
+Conservation efforts can address density dependent factors by reducing competition for resources, managing predation and disease transmission, and improving habitat quality. By mitigating the negative effects of high population densities, conservation efforts can promote sustainable population growth and maintain healthy ecosystems.
What is the relationship between carrying capacity and density dependent factors?
+Carrying capacity, which is the maximum population size that an environment can sustain indefinitely, is closely related to density dependent factors. As a population approaches its carrying capacity, density dependent factors such as increased competition for resources and predation become more pronounced, eventually leading to a stabilization of the population size.