Dihybrid Cross Punnett Square
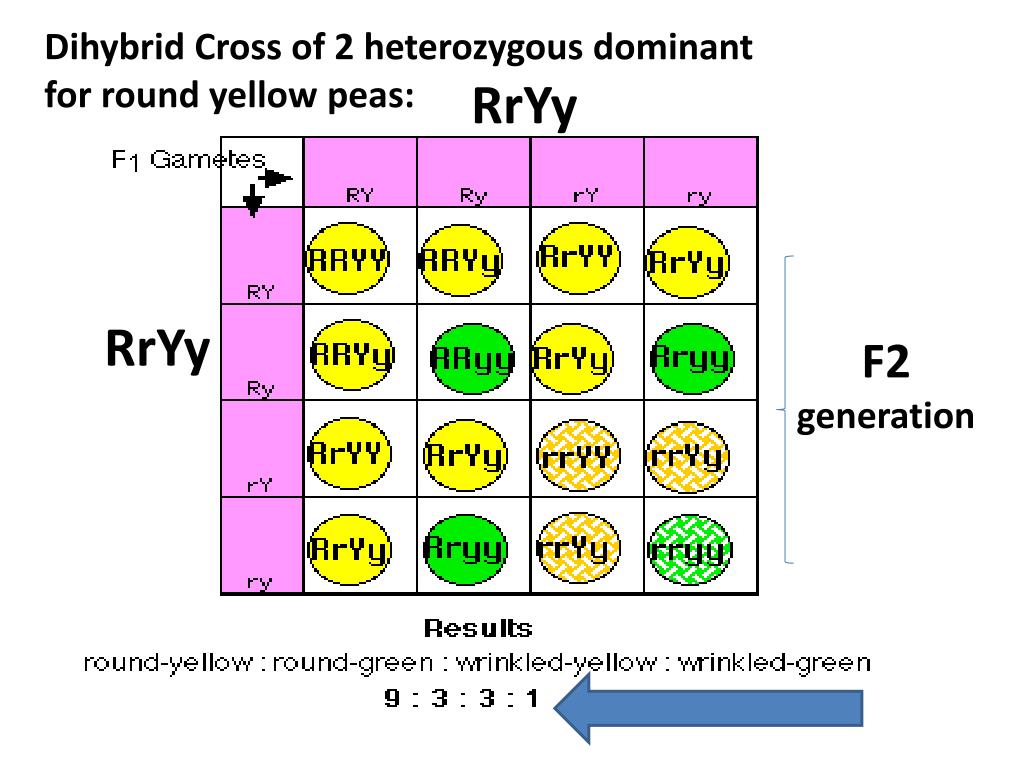
The dihybrid cross is a fundamental concept in genetics, used to predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring. This technique involves crossing two parents that are heterozygous for two different genes, resulting in a complex Punnett square that takes into account the interactions between the two genes. In this article, we will delve into the world of dihybrid crosses, exploring the theory, application, and interpretation of Punnett squares in this context.
Key Points
- The dihybrid cross involves crossing two parents that are heterozygous for two different genes.
- The Punnett square for a dihybrid cross is a 4x4 grid that takes into account the interactions between the two genes.
- The dihybrid cross can be used to predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring.
- The technique is commonly used in genetics to study the inheritance of traits and to predict the likelihood of certain genetic combinations.
- The dihybrid cross can also be used to study the interactions between different genes and to identify genetic linkages.
Understanding the Dihybrid Cross

A dihybrid cross is a type of genetic cross that involves two parents that are heterozygous for two different genes. For example, let’s consider two genes: one that controls flower color (R/r) and another that controls plant height (T/t). The parents are heterozygous for both genes, meaning they have one copy of each allele (RrTt). The dihybrid cross involves crossing these two parents to produce offspring that inherit a combination of these genes.
Constructing the Punnett Square
To predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in the offspring, we use a Punnett square. The Punnett square for a dihybrid cross is a 4x4 grid that takes into account the interactions between the two genes. The grid is constructed by listing all possible combinations of alleles for the two genes, with each row and column representing a different allele. The resulting grid shows all possible genotypes and their corresponding probabilities.
| Genotype | Probability |
|---|---|
| RRTT | 1/16 |
| RRTt | 2/16 |
| RRtt | 1/16 |
| RrTT | 2/16 |
| RrTt | 4/16 |
| Rrtt | 2/16 |
| rrTT | 1/16 |
| rrTt | 2/16 |
| rrtt | 1/16 |

Interpreting the Punnett Square

Once we have constructed the Punnett square, we can interpret the results to predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in the offspring. The grid shows all possible genotypes and their corresponding probabilities, allowing us to identify the most likely genotypes and phenotypes. For example, the Punnett square above shows that the probability of the offspring having the genotype RRTT is 1⁄16, while the probability of having the genotype RrTt is 4⁄16.
Phenotypic Ratios
In addition to predicting genotypic ratios, the dihybrid cross Punnett square can also be used to predict phenotypic ratios. By analyzing the grid, we can identify the probability of each phenotype and predict the phenotypic ratio of the offspring. For example, if we are studying the inheritance of flower color and plant height, the Punnett square can be used to predict the probability of each phenotype (e.g., tall plants with red flowers, short plants with white flowers, etc.).
Applications of the Dihybrid Cross
The dihybrid cross is a fundamental technique in genetics, with a wide range of applications in fields such as plant breeding, animal breeding, and medicine. The technique can be used to study the inheritance of traits, to predict the likelihood of certain genetic combinations, and to identify genetic linkages. In addition, the dihybrid cross can be used to develop new crop varieties with desirable traits, such as disease resistance or improved yield.
What is the purpose of a dihybrid cross?
+The purpose of a dihybrid cross is to predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring, taking into account the interactions between two different genes.
How is the Punnett square constructed for a dihybrid cross?
+The Punnett square for a dihybrid cross is constructed by listing all possible combinations of alleles for the two genes, with each row and column representing a different allele.
What are the applications of the dihybrid cross?
+The dihybrid cross has a wide range of applications in fields such as plant breeding, animal breeding, and medicine, including the study of trait inheritance, prediction of genetic combinations, and identification of genetic linkages.
Meta Description: Learn about the dihybrid cross and how to construct a Punnett square to predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring. Discover the applications of this fundamental technique in genetics. (149 characters)



