How Does Condensation Work
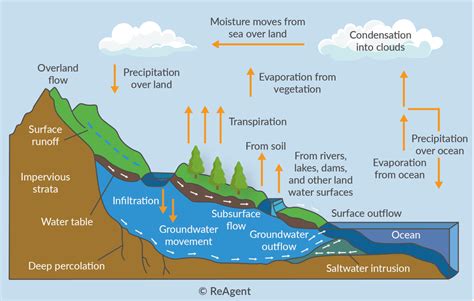
Condensation is a fundamental process in the Earth's water cycle, playing a crucial role in shaping our environment and influencing various aspects of our daily lives. At its core, condensation is the transformation of water vapor into liquid water, a process that occurs when the air reaches its dew point. The dew point is the temperature at which the air becomes saturated with water vapor and can no longer hold any more moisture. As the air cools down to its dew point, the water vapor in the air condenses into tiny droplets, forming fog, dew, or precipitation.
The process of condensation is intricately linked to the principles of thermodynamics and the behavior of gases. When the temperature of the air decreases, the molecules of water vapor slow down and come closer together, eventually forming droplets. This process is facilitated by the presence of condensation nuclei, which are tiny particles in the air that provide a surface for the water vapor to condense onto. Common condensation nuclei include dust particles, salt crystals, and pollutants. The size and type of these nuclei can significantly impact the efficiency of the condensation process, with larger nuclei generally leading to the formation of larger droplets.
Key Points
- Condensation occurs when the air reaches its dew point, causing water vapor to transform into liquid water.
- The dew point is the temperature at which the air becomes saturated with water vapor and can no longer hold any more moisture.
- Condensation is facilitated by the presence of condensation nuclei, which provide a surface for the water vapor to condense onto.
- The size and type of condensation nuclei can impact the efficiency of the condensation process.
- Condensation plays a crucial role in the Earth's water cycle, influencing weather patterns, climate, and ecosystems.
Types of Condensation
There are several types of condensation, each occurring under different conditions and playing a unique role in the Earth’s water cycle. One of the most common forms of condensation is evaporative condensation, which occurs when the air is cooled from below, such as when it passes over a cool surface or comes into contact with a cold object. This type of condensation is often observed in the formation of dew, which is an essential source of water for many plants and animals. Another type of condensation is adiabatic condensation, which occurs when the air is cooled from within, such as when it rises to higher altitudes and expands, causing the temperature to decrease.
Condensation in Cloud Formation
Condensation plays a critical role in the formation of clouds, which are collections of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air. Clouds form when the air is cooled to its dew point, causing the water vapor to condense into droplets. The type and amount of condensation that occurs in clouds can significantly impact the weather, with different types of clouds forming under different conditions. For example, cumulus clouds form when warm air rises and cools, causing the water vapor to condense into large, puffy droplets. In contrast, stratus clouds form when a layer of cool air is trapped under a layer of warm air, causing the water vapor to condense into a uniform, flat layer.
| Cloud Type | Formation Conditions | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Cumulus | Warm air rises and cools | Large, puffy droplets |
| Stratus | Cool air trapped under warm air | Uniform, flat layer |
| Cirrus | Cold air at high altitudes | Ice crystals, feathery appearance |

Importance of Condensation

Condensation is a vital component of the Earth’s water cycle, playing a crucial role in shaping our environment and influencing various aspects of our daily lives. The process of condensation helps to regulate the Earth’s climate, with the formation of clouds and precipitation helping to cool the planet and distribute heat around the globe. Condensation also plays a critical role in the formation of groundwater, with the infiltration of precipitation into the soil helping to recharge aquifers and maintain the health of ecosystems.
The importance of condensation is not limited to its role in the water cycle; it also has significant implications for human health and well-being. For example, the formation of fog and dew can help to reduce the risk of respiratory diseases, while the presence of condensation on surfaces can help to reduce the risk of heat stress and other heat-related illnesses. Furthermore, condensation is essential for the formation of precipitation, which is critical for agriculture, industry, and human consumption.
Applications of Condensation
The process of condensation has numerous applications in various fields, including engineering, architecture, and environmental science. For example, condensation heat transfer is used in the design of heat exchangers, which are critical components of power plants, refrigeration systems, and air conditioning units. Condensation is also used in the distillation process, which is essential for the production of drinking water, fuels, and other chemicals. Additionally, condensation is used in the dehumidification process, which is critical for maintaining the health and comfort of buildings and their occupants.
What is the difference between condensation and evaporation?
+Condensation is the process by which water vapor transforms into liquid water, while evaporation is the process by which liquid water transforms into water vapor.
What are the main factors that influence condensation?
+The main factors that influence condensation include temperature, humidity, and the presence of condensation nuclei.
What are the applications of condensation in engineering?
+Condensation has numerous applications in engineering, including the design of heat exchangers, distillation processes, and dehumidification systems.
In conclusion, condensation is a complex and multifaceted process that plays a critical role in the Earth’s water cycle and has numerous applications in various fields. Understanding the principles of condensation is essential for predicting weather patterns, managing water resources, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. By recognizing the importance of condensation and its applications, we can work towards developing more sustainable and efficient solutions for the challenges facing our planet.



