How To Find Neutrons In An Element

The process of finding neutrons in an element involves understanding the basic structure of atoms and the role of neutrons within the nucleus. Atoms are the building blocks of matter, and they consist of three main components: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, which is the central part of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms, known as the atomic number.
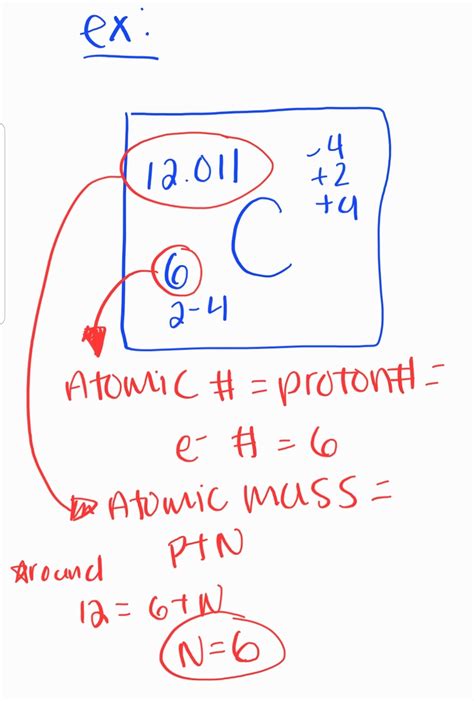
To find the number of neutrons in an element, one must first know the atomic mass of the element and its atomic number. The atomic mass is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. The atomic number, as mentioned, is the number of protons. By subtracting the atomic number from the atomic mass, one can determine the number of neutrons. However, it's essential to note that the atomic mass listed for an element on the periodic table is usually an average mass, which takes into account the natural abundance of different isotopes of that element. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Key Points
- The atomic number of an element determines its identity and is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus.
- The atomic mass is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and can vary among isotopes of the same element.
- Neutrons contribute to the mass of an atom but not to its charge, as they are neutral particles.
- Understanding the number of neutrons is crucial for nuclear physics and chemistry applications.
- Isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties but can differ in physical properties and nuclear stability.
Calculating the Number of Neutrons

The calculation of neutrons in an atom is straightforward once the atomic mass and atomic number are known. For example, if we consider an atom of carbon-14, the atomic number of carbon is 6 (since carbon always has 6 protons), and the atomic mass of this particular isotope is 14. To find the number of neutrons, we subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass: 14 (atomic mass) - 6 (atomic number) = 8 neutrons.
Isotopes and Neutron Variation
It’s crucial to understand that while the number of protons in an atom of a given element is always the same, the number of neutrons can vary, leading to different isotopes. These isotopes have the same chemical properties because the chemical behavior of an element is determined by the number of electrons, which in turn is equal to the number of protons in a neutral atom. However, isotopes can differ significantly in their physical properties and stability. For instance, carbon has several isotopes, including carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14, each with a different number of neutrons but the same number of protons.
| Isotope | Atomic Number | Atomic Mass | Number of Neutrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-12 | 6 | 12 | 6 |
| Carbon-13 | 6 | 13 | 7 |
| Carbon-14 | 6 | 14 | 8 |
Practical Applications of Neutron Knowledge

Knowing the number of neutrons in an atom has significant implications for various fields, including nuclear physics, chemistry, and engineering. In nuclear physics, the number of neutrons can affect the stability of an isotope, with certain combinations of protons and neutrons leading to more stable nuclei. In chemistry, understanding isotopes and their neutron numbers is crucial for tracing chemical reactions, understanding metabolic pathways, and analyzing the composition of materials.
In engineering, the knowledge of neutrons and isotopes is vital for the development of nuclear reactors, where the balance between different isotopes can significantly impact the reactor's efficiency and safety. Moreover, isotopes are used in medical treatments, such as radiation therapy, and in industrial applications, such as sterilization of medical instruments and food irradiation.
Nuclear Stability and Radioactivity
The number of neutrons in an atom’s nucleus can determine whether an isotope is stable or radioactive. If an isotope has too many or too few neutrons relative to the number of protons, it can be unstable and undergo radioactive decay. This process involves the emission of radiation as the nucleus adjusts to a more stable configuration. Understanding the role of neutrons in nuclear stability is crucial for predicting the half-life of radioactive isotopes and for the safe handling and application of radioactive materials.
What determines the number of neutrons in an atom?
+The number of neutrons in an atom is determined by the specific isotope of an element. Each isotope has a unique combination of protons and neutrons, with the protons defining the element and the neutrons contributing to the isotope's mass and stability.
Why are neutrons important in nuclear reactions?
+Neutrons play a crucial role in nuclear reactions, including fission and fusion, as they can induce reactions when absorbed by nuclei. Their presence or absence can significantly affect the outcome of these processes, making them a key factor in nuclear physics and engineering applications.
How do scientists use knowledge of neutrons in practical applications?
+Scientists utilize knowledge of neutrons in various practical applications, including the development of nuclear power plants, medical treatments like radiation therapy, and industrial processes such as food irradiation. Understanding neutrons and their role in isotopes is essential for the safe and efficient use of these technologies.
In conclusion, finding neutrons in an element requires a basic understanding of atomic structure and the relationship between protons, neutrons, and atomic mass. The calculation of neutrons involves subtracting the atomic number from the atomic mass, but it’s also crucial to consider the concept of isotopes and how the variation in neutron numbers affects the physical properties and stability of atoms. The practical applications of this knowledge span multiple disciplines, from nuclear physics and chemistry to engineering and medicine, highlighting the importance of understanding neutrons for both theoretical insights and real-world applications.