Leg Muscles Labeled

The human leg is a complex structure comprising multiple muscles that work in tandem to facilitate movement, stability, and balance. Understanding the anatomy of the leg muscles is crucial for athletes, physiotherapists, and individuals seeking to improve their overall lower body strength and flexibility. In this article, we will delve into the primary muscles of the leg, their functions, and the importance of maintaining their health.
Anterior Compartment of the Leg

The anterior compartment of the leg contains muscles responsible for dorsiflexion (lifting the foot upwards) and toe extension. The primary muscles in this compartment include:
- Tibialis anterior: This muscle is responsible for dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot.
- Extensor hallucis longus: As its name suggests, this muscle extends the big toe and assists in dorsiflexion of the foot.
- Extensor digitorum longus: This muscle extends the toes and helps in dorsiflexion of the foot.
- Peroneus tertius: Although primarily involved in foot eversion (rotating the foot outwards), it also assists in dorsiflexion.
Lateral Compartment of the Leg
The lateral compartment houses muscles primarily involved in foot eversion. The key muscles in this compartment are:
- Peroneus longus: This muscle everts the foot and supports the arch during weight-bearing activities.
- Peroneus brevis: Similar to the peroneus longus, the peroneus brevis muscle everts the foot.
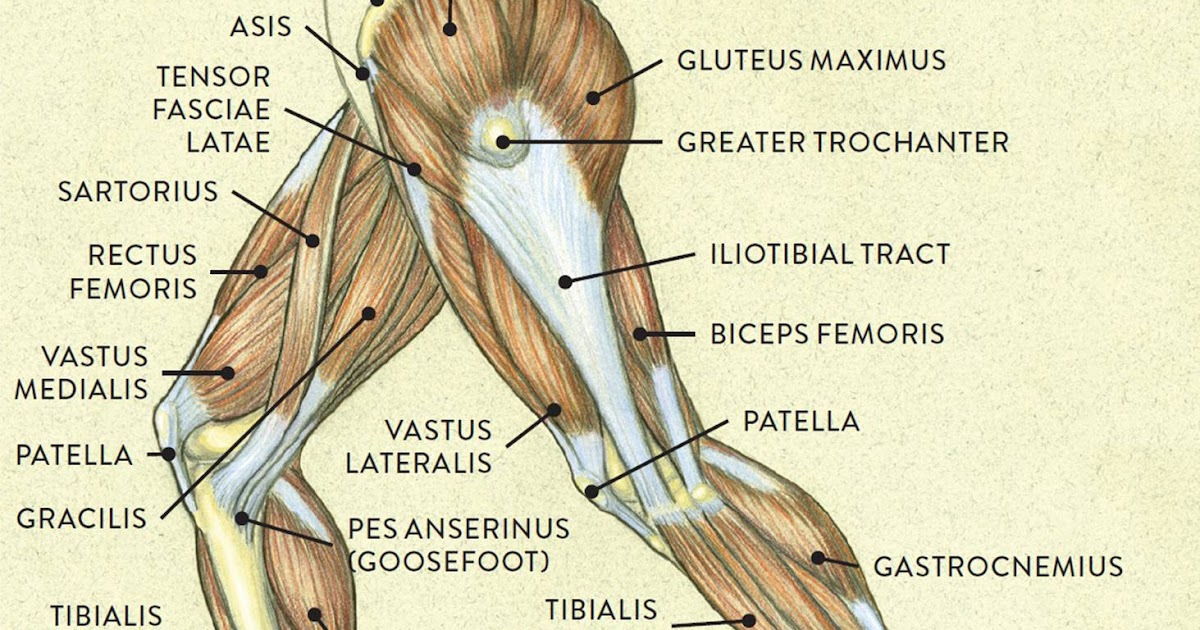
Posterior Compartment of the Leg
The posterior compartment is divided into deep and superficial layers, containing muscles crucial for plantarflexion (pointing the foot downwards) and toe flexion.
Superficial Layer
The superficial layer of the posterior compartment includes:
- Gastrocnemius: This muscle is responsible for plantarflexion of the foot and flexion of the knee.
- Soleus: The soleus muscle plantarflexes the foot and plays a significant role in standing and walking.
- Plantaris: Although small, the plantaris muscle assists in plantarflexion and knee flexion.
Deep Layer
The deep layer of the posterior compartment contains:
- Popliteus: This muscle is involved in unlocking the knee by rotating the femur on the tibia.
- Flexor hallucis longus: As its name indicates, this muscle flexes the big toe and assists in plantarflexion of the foot.
- Flexor digitorum longus: This muscle flexes the toes and supports plantarflexion of the foot.
- Tibialis posterior: The tibialis posterior muscle supports the arch of the foot, inverts the foot, and assists in plantarflexion.
| Muscle Group | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Anterior Compartment | Dorsiflexion and toe extension |
| Lateral Compartment | Foot eversion |
| Posterior Compartment (Superficial) | Plantarflexion and knee flexion |
| Posterior Compartment (Deep) | Plantarflexion, toe flexion, and support of the foot arch |
Key Points
- The leg muscles are categorized into anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments, each serving distinct functions.
- The anterior compartment muscles are primarily responsible for dorsiflexion and toe extension.
- The lateral compartment contains muscles that evert the foot.
- The posterior compartment, divided into superficial and deep layers, contains muscles crucial for plantarflexion and toe flexion.
- A balanced understanding of these muscles and their functions is vital for maintaining leg health and preventing injuries.
In conclusion, the muscles of the leg work in harmony to facilitate a wide range of movements and maintain posture. Recognizing the roles and importance of each muscle group can inform exercise routines, rehabilitation strategies, and overall health maintenance. Whether for athletic performance or everyday mobility, a deep understanding of leg anatomy is indispensable.
What is the primary function of the tibialis anterior muscle?
+The primary function of the tibialis anterior muscle is dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot, playing a crucial role in activities such as walking and running.
How do the muscles of the posterior compartment contribute to overall leg function?
+The muscles of the posterior compartment, including both the superficial and deep layers, are vital for plantarflexion, toe flexion, and support of the foot arch, thereby contributing significantly to standing, walking, and running activities.
What is the role of the peroneus longus and brevis muscles in foot movement?
+The peroneus longus and brevis muscles are primarily involved in foot eversion, which is the movement of the foot outwards, away from the midline of the body. They also play a role in supporting the arch of the foot during weight-bearing activities.