Limited Government Examples
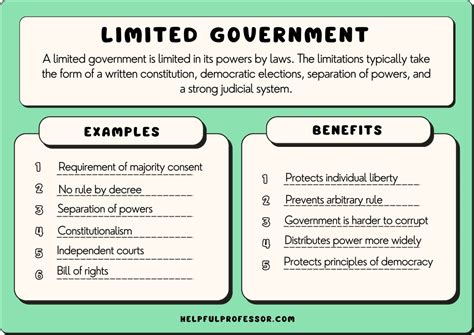
The concept of limited government has been a cornerstone of political philosophy and practice for centuries, emphasizing the importance of restricting the power of the government to protect individual rights and freedoms. This approach to governance is based on the idea that individuals and communities are better equipped to manage their own affairs than a centralized authority. In the context of limited government, several examples illustrate its implementation and benefits.
Historical Foundations of Limited Government

One of the earliest and most influential examples of limited government can be found in the Magna Carta, signed in 1215 by King John of England. This document established key principles such as the rule of law, due process, and protection of individual rights from arbitrary governmental actions. The Magna Carta’s emphasis on limiting the monarch’s power in favor of the nobility and, by extension, the common people, laid the groundwork for subsequent political and legal developments in the concept of limited government.
The American Experience
The United States Constitution and the Bill of Rights are quintessential examples of limited government in action. The Constitution’s system of checks and balances among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches is designed to prevent any one branch from dominating the others, thereby limiting the potential for abuses of power. The Bill of Rights, with its guarantees of freedom of speech, press, assembly, and the right to bear arms, among others, further restricts government overreach into personal and public life.
| Key Document | Provisions |
|---|---|
| Magna Carta | Established rule of law, due process, and protection of individual rights |
| US Constitution | System of checks and balances, separation of powers |
| Bill of Rights | Guarantees of individual freedoms and rights |

Modern Applications and Challenges

In modern times, the concept of limited government continues to evolve, with debates focusing on the appropriate role of government in the economy, healthcare, education, and national security. For instance, proponents of limited government often argue for lower taxes, reduced regulatory burdens on businesses, and a more minimalist approach to social welfare programs. Critics, on the other hand, may argue that such policies can exacerbate income inequality, undermine public health and education, and compromise national security.
Economic Perspectives
Economists like Milton Friedman and Friedrich Hayek have been influential in arguing for limited government intervention in economic matters, advocating for free market principles and minimal regulation. They contend that government interference can lead to inefficiencies, stifle innovation, and create unintended consequences. In contrast, Keynesian economists argue for a more active role of government in stabilizing the economy during times of recession or high unemployment, suggesting that government spending and fiscal policies can help mitigate economic downturns.
Key Points
- The concept of limited government is rooted in historical documents like the Magna Carta and the US Constitution.
- Checks and balances and the separation of powers are key mechanisms for limiting government power.
- Debates over limited government involve discussions on the appropriate role of government in the economy, healthcare, education, and national security.
- Economic perspectives on limited government range from advocating for free market principles to supporting government intervention for economic stability.
- Challenges to implementing limited government include balancing individual freedoms with collective needs and addressing issues of inequality and access to services.
As the world navigates complex challenges such as climate change, pandemics, and economic inequality, the concept of limited government must be considered in the context of global interdependence and the need for collective action. While the principles of limited government remain crucial for protecting individual rights and promoting economic efficiency, they must be balanced against the need for effective governance and collective problem-solving at local, national, and international levels.
What are the primary mechanisms for limiting government power in the US Constitution?
+The primary mechanisms include the system of checks and balances among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches, as well as the separation of powers and the Bill of Rights.
How do proponents of limited government approach economic policy?
+Proponents often advocate for free market principles, lower taxes, and reduced regulatory burdens, arguing that these policies promote economic efficiency and individual freedom.
What are some of the challenges in implementing limited government principles in modern societies?
+Challenges include balancing individual freedoms with collective needs, addressing issues of inequality and access to services, and navigating the complexities of global interdependence and the need for collective action on issues like climate change and public health.
In conclusion, the concept of limited government is complex and multifaceted, with historical roots and ongoing relevance in contemporary political and economic debates. As societies continue to evolve and face new challenges, the principles of limited government will remain a crucial part of the discussion on how to balance individual rights and freedoms with the need for effective governance and collective action.