Low Residue Foods
For individuals dealing with certain gastrointestinal conditions or undergoing specific medical treatments, managing their diet is crucial for alleviating symptoms and ensuring proper nutrition. One dietary approach that has gained attention for its potential benefits in these situations is the low residue diet, also known as the low fiber diet. This eating plan is designed to reduce the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, thereby minimizing the workload on the digestive system. In this article, we will delve into the concept of low residue foods, their role in managing gastrointestinal health, and provide guidance on how to incorporate them into your diet.
Key Points
- The low residue diet is often recommended for individuals with gastrointestinal conditions such as Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) to help manage symptoms.
- Foods that are low in residue include tender meats, refined grains, and well-cooked vegetables, which are easier to digest.
- A well-planned low residue diet can help reduce symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders but should be undertaken under the guidance of a healthcare provider or dietitian.
- It's essential to balance the need for a low residue diet with the importance of maintaining adequate nutrition to support overall health.
- Gradually introducing high residue foods back into the diet after a period of following a low residue diet can help in assessing tolerance and managing gastrointestinal health.
Understanding Low Residue Foods
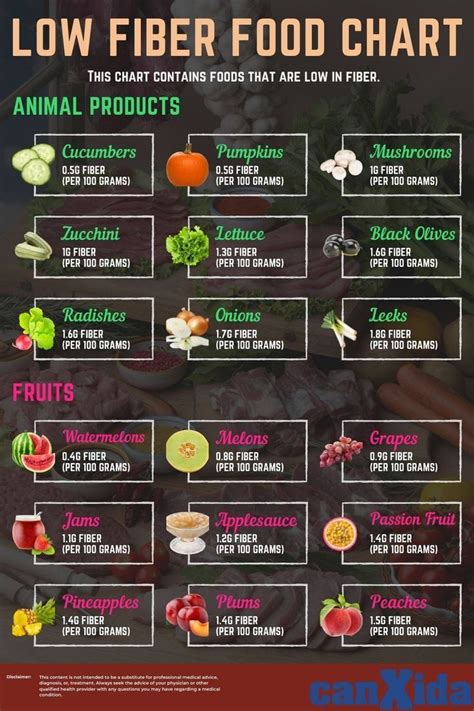
Low residue foods are those that are easily digestible and leave minimal waste in the digestive system. They are typically low in fiber, which is a key component that distinguishes them from high residue or high fiber foods. The logic behind consuming low residue foods, especially for individuals with certain gastrointestinal issues, is to give the digestive system a break by reducing the amount of work it has to do. This can be particularly beneficial during flare-ups of conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, where the digestive system is already under stress.
Examples of Low Residue Foods
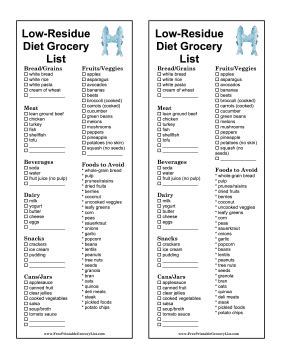
Examples of low residue foods include:
- Tender meats like chicken, fish, and turkey
- Refined grains such as white bread, pasta, and rice
- Well-cooked vegetables like carrots, green beans, and potatoes
- Fruits that are low in fiber and seeds, such as bananas and avocados
- Dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese, which are low in fiber
These foods are chosen for their ease of digestion and low fiber content, which can help in minimizing the amount of residue that reaches the colon.
| Food Category | Examples of Low Residue Foods |
|---|---|
| Meat/Protein | Chicken, turkey, fish, eggs |
| Grains | White bread, white rice, plain crackers |
| Vegetables | Cooked carrots, green beans, peeled potatoes |
| Fruits | Bananas, avocados, melons (without seeds) |
| Dairy | Milk, yogurt, cheese |

Implementing a Low Residue Diet

Implementing a low residue diet requires careful planning to ensure that nutritional needs are met while minimizing gastrointestinal stress. Here are some steps to consider:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider or Dietitian: Before starting any new diet, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized advice based on your health status, nutritional needs, and lifestyle.
- Keep a Food Diary: Keeping track of the foods you eat and how they affect your symptoms can be incredibly helpful in identifying which foods are problematic and which are well-tolerated.
- Gradually Introduce Foods: When reintroducing high residue foods into your diet, do so gradually. This can help your digestive system adjust and reduce the risk of exacerbating symptoms.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for digestive health. Ensure you’re drinking enough water throughout the day.
Challenges and Considerations
While a low residue diet can be beneficial, there are challenges and considerations to keep in mind. One of the primary concerns is ensuring that the diet is well-balanced and provides all the necessary nutrients. Fiber, for example, plays a crucial role in digestive health and satiety. Reducing fiber intake significantly can lead to constipation and may impact blood sugar levels and cholesterol levels over time.
Furthermore, a low residue diet may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those without gastrointestinal conditions. For healthy individuals, a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods is generally recommended for optimal nutrition and health.
What is the primary goal of a low residue diet?
+The primary goal of a low residue diet is to reduce the amount of undigested food that reaches the colon, thereby minimizing the workload on the digestive system and alleviating symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders.
How long should I follow a low residue diet?
+The duration of a low residue diet depends on the individual's health condition and response to the diet. It's essential to follow the advice of a healthcare provider or dietitian regarding the duration and any adjustments to the diet.
Can I still get enough nutrients on a low residue diet?
+Yes, it's possible to get enough nutrients on a low residue diet if it's well-planned. However, it may require careful selection of foods and possibly supplementation to ensure all nutritional needs are met.
In conclusion, low residue foods play a significant role in the management of gastrointestinal health, particularly for individuals with conditions like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and IBS. By understanding which foods are low in residue and how to incorporate them into your diet, you can take a proactive step towards managing your symptoms and improving your quality of life. Always remember to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian before making any significant changes to your diet to ensure that your nutritional needs are met and that the diet is tailored to your specific health requirements.



