Molecular Compounds Chemistry
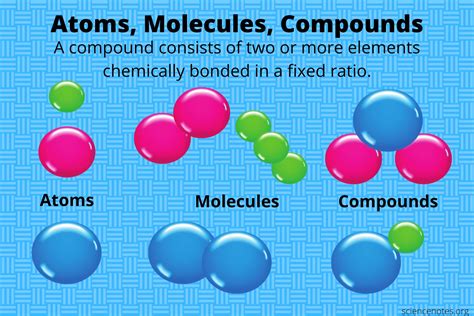
Molecular compounds are a fundamental concept in chemistry, referring to chemical substances that are composed of two or more different elements, typically in a fixed ratio, and are held together by covalent bonds. These compounds are a crucial part of organic and inorganic chemistry, and their understanding is essential for various fields, including biochemistry, materials science, and pharmaceuticals. The study of molecular compounds involves understanding their formation, properties, and reactions, which are influenced by the types of bonds and the molecular structure.
The formation of molecular compounds can be attributed to the sharing of electrons between atoms, leading to the formation of covalent bonds. This sharing can occur between atoms of the same element, such as in oxygen (O2), or between atoms of different elements, such as in water (H2O) or carbon dioxide (CO2). The properties of molecular compounds, including their melting and boiling points, solubility, and reactivity, are determined by the strength and polarity of these covalent bonds, as well as the molecular shape and size.
Key Points
- Molecular compounds are formed through covalent bonds between atoms of the same or different elements.
- The properties of molecular compounds are influenced by the strength and polarity of covalent bonds and molecular structure.
- Understanding molecular compounds is crucial for fields like biochemistry, materials science, and pharmaceuticals.
- Molecular compounds can exhibit a wide range of properties, including variability in melting and boiling points and solubility.
- The study of molecular compounds involves analyzing their formation, properties, and reactions.
Types of Molecular Compounds

Molecular compounds can be categorized based on their composition and the types of bonds they contain. Binary molecular compounds, for instance, are composed of two different elements, such as hydrogen chloride (HCl) or carbon monoxide (CO). Ternary molecular compounds contain three different elements, such as ammonia (NH3) or sulfur dioxide (SO2). The classification and naming of molecular compounds follow specific rules, with the use of prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound.
Naming Molecular Compounds
The naming of molecular compounds involves the use of prefixes to denote the number of atoms of each element present. For example, in the compound SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride), “hexa-” indicates six fluorine atoms. This systematic approach to naming helps in the identification and communication of molecular compounds among chemists. Understanding the rules for naming molecular compounds is essential for accurately describing and categorizing these substances.
| Compound | Formula | Name |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Chloride | HCl | Hydrogen Monochloride |
| Carbon Dioxide | CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| Sulfur Trioxide | SO3 | Sulfur Trioxide |
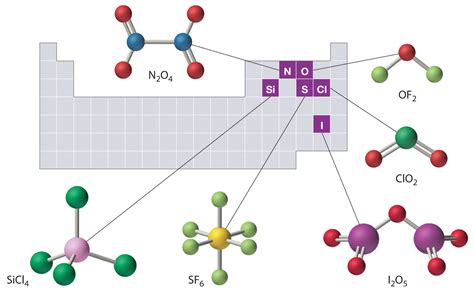
Properties of Molecular Compounds
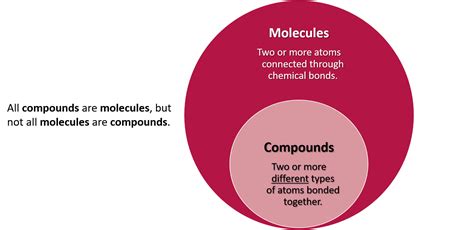
The properties of molecular compounds are determined by the types of bonds between the atoms and the shape of the molecule. Polar molecules, such as water, have a partial positive charge on one side and a partial negative charge on the other, leading to higher melting and boiling points due to the stronger intermolecular forces. Nonpolar molecules, like carbon dioxide, have symmetrical charge distributions, resulting in lower melting and boiling points. The solubility of molecular compounds in water or other solvents is also influenced by their polarity, with polar compounds generally being more soluble in water.
Reactions of Molecular Compounds
Molecular compounds undergo various chemical reactions, including combustion, synthesis, and decomposition reactions. These reactions involve the breaking and forming of covalent bonds, leading to the formation of new compounds. Understanding the reactivity of molecular compounds is crucial for predicting the outcomes of chemical reactions and for the synthesis of new materials and substances.
The study of molecular compounds and their reactions is deeply rooted in the principles of quantum mechanics and thermodynamics. The application of these principles allows chemists to predict the stability and reactivity of molecular compounds, as well as the conditions under which chemical reactions occur. This knowledge is fundamental for the development of new technologies and products in fields such as energy, healthcare, and manufacturing.
What are molecular compounds and how are they formed?
+Molecular compounds are chemical substances composed of two or more different elements held together by covalent bonds. They are formed through the sharing of electrons between atoms, which can be of the same element or different elements.
How are molecular compounds named?
+Molecular compounds are named using a systematic approach that involves the use of prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. This method helps in the accurate identification and communication of molecular compounds.
What factors influence the properties of molecular compounds?
+The properties of molecular compounds, such as melting and boiling points, solubility, and reactivity, are influenced by the strength and polarity of the covalent bonds and the molecular structure.
In conclusion, molecular compounds are a vital part of chemistry, with their study and understanding being essential for various fields and applications. The formation, properties, and reactions of these compounds are influenced by the types of bonds and the molecular structure, making the study of molecular compounds both fascinating and complex. Through the continued exploration and understanding of molecular compounds, scientists and researchers can develop new materials, technologies, and solutions that address some of the world’s most pressing challenges.



