Western Front History
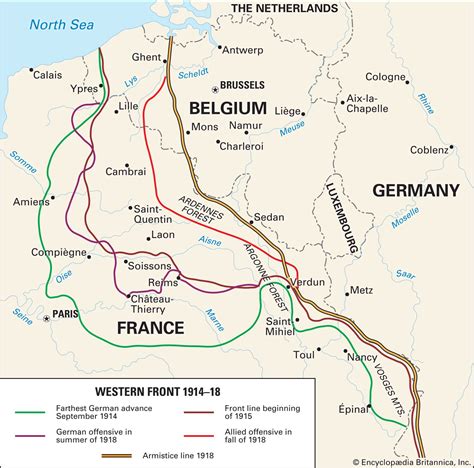
The Western Front, a term used to describe the battlefields of World War I that stretched from the North Sea to the Swiss border, was one of the most pivotal and devastating theaters of conflict in human history. The front, which was established in 1914 and remained relatively stable until the final months of the war, witnessed some of the most brutal and transformative battles of the 20th century. From the early trenches and massacres of 1914 to the Armistice of November 11, 1918, the Western Front was a place of unrelenting violence, unprecedented destruction, and profound human suffering.
The roots of the Western Front can be traced back to the complex system of alliances and rivalries that existed in Europe during the early 20th century. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary in June 1914 sparked a chain reaction of diplomatic crises and military mobilizations that eventually led to the outbreak of war. As the conflict escalated, the German army, seeking to quickly defeat France and then turn to face Russia, launched a massive invasion of neutral Belgium, which prompted the United Kingdom to declare war on Germany. The resulting clash of armies in the late summer of 1914 led to the establishment of the Western Front, a 470-mile-long (750 km) stretch of trenches, barbed wire, and fortifications that would remain largely unchanged for the next four years.
Key Points
- The Western Front was established in 1914 and remained relatively stable until the final months of World War I.
- The front witnessed some of the most brutal and transformative battles of the 20th century, including the Battle of the Somme and the Battle of Verdun.
- The war on the Western Front was characterized by the use of trench warfare, machine guns, and poison gas, which resulted in massive casualties and unprecedented destruction.
- The United States entered the war in 1917, providing significant military and economic support to the Allied powers and helping to turn the tide of the conflict.
- The Armistice of November 11, 1918, marked the end of hostilities on the Western Front, but the war's legacy continued to shape European politics and society for generations to come.
The Trenches and the Nature of Modern Warfare

The Western Front was marked by the widespread use of trench warfare, a form of combat that had been used to a limited extent in previous conflicts but became the dominant mode of warfare during World War I. The trenches, which were often dirty, crowded, and prone to flooding, were a far cry from the romanticized battlefields of earlier wars. Soldiers on both sides of the conflict were forced to endure months of boredom, discomfort, and fear, punctuated by periods of intense violence and chaos. The trenches also gave rise to a new kind of warfare, one that was characterized by the use of machine guns, poison gas, and other technologies that made it possible to kill large numbers of people quickly and efficiently.
The introduction of new technologies, such as tanks, airplanes, and submarines, also transformed the nature of warfare on the Western Front. The development of tanks, for example, allowed armies to break through enemy lines and restore mobility to the battlefield. The use of airplanes, meanwhile, enabled armies to gather intelligence, conduct reconnaissance, and launch aerial attacks on enemy positions. The introduction of submarines, which were used by Germany to attack Allied shipping, also played a significant role in the war, particularly in the early years.
The Major Battles of the Western Front
The Western Front was the site of some of the most significant and bloody battles of World War I. The Battle of the Somme, which was fought in the summer of 1916, was one of the deadliest battles in human history, with over 1 million casualties on both sides. The Battle of Verdun, which was fought from February to December 1916, was another major conflict, with over 700,000 casualties. The Battle of Passchendaele, which was fought in the summer and fall of 1917, was also a significant battle, with over 400,000 casualties. These battles, along with others, such as the Battle of the Marne and the Battle of Amiens, helped to shape the course of the war and ultimately contributed to the Allied victory.
| Battle | Date | Casualties |
|---|---|---|
| Battle of the Somme | July 1, 1916 - November 18, 1916 | 1,000,000+ |
| Battle of Verdun | February 21, 1916 - December 18, 1916 | 700,000+ |
| Battle of Passchendaele | July 31, 1917 - November 10, 1917 | 400,000+ |
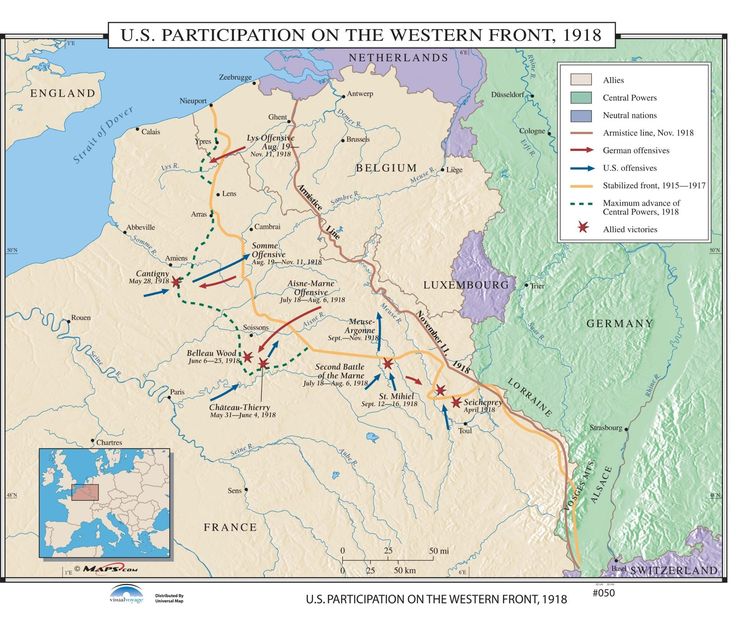
The United States and the Western Front
The United States entered World War I in April 1917, after Germany resumed unrestricted submarine warfare and sank several American ships. The U.S. contribution to the war effort was significant, with over 2 million American soldiers serving on the Western Front. The U.S. Army played a major role in several key battles, including the Battle of Belleau Wood and the Battle of the Argonne Forest. The American contribution helped to turn the tide of the war, as the influx of fresh troops and supplies enabled the Allies to launch a series of successful offensives that eventually led to the defeat of Germany.
The impact of the Western Front on American society was also significant. The war marked a major turning point in American history, as the country emerged from its traditional isolationism and became a major world power. The war also had a profound impact on American culture, as the experiences of soldiers on the Western Front influenced literature, art, and music for generations to come.
The Armistice and the Aftermath of the War
The Armistice of November 11, 1918, marked the end of hostilities on the Western Front, but the war’s legacy continued to shape European politics and society for generations to come. The Treaty of Versailles, which was signed in June 1919, imposed harsh penalties on Germany, including significant territorial losses and reparations. The treaty also established the League of Nations, an international organization dedicated to promoting peace and preventing future wars. However, the treaty’s failure to provide a lasting peace and its role in contributing to the rise of Nazi Germany are widely acknowledged by historians.
The Western Front also had a profound impact on the soldiers who fought there. The war marked a major turning point in the history of warfare, as the introduction of new technologies and tactics led to unprecedented levels of violence and destruction. The war also had a profound psychological impact on soldiers, many of whom suffered from what would later be recognized as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The experiences of soldiers on the Western Front continue to influence literature, art, and popular culture to this day.
What was the significance of the Western Front in World War I?
+The Western Front was the main theater of conflict in World War I, with the war being fought between the Allied Powers (France, Britain, and the United States) and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). The front was characterized by the use of trench warfare, machine guns, and poison gas, and was the site of some of the most significant and bloody battles of the war.
What were the major battles of the Western Front?
+The major battles of the Western Front included the Battle of the Somme, the Battle of Verdun, the Battle of Passchendaele, and the Battle of Amiens. These battles were significant not only for their military importance but also for their impact on the course of the war and the eventual Allied victory.
How did the United States contribute to the war effort on the Western Front?
+The United States entered World War I in April 1917 and played a significant role in the war effort on the Western Front. The U.S. Army contributed over 2 million soldiers to the front, and the country provided significant economic and military support to the Allied powers. The American contribution helped to turn the tide of the war and contributed to the eventual Allied victory.
