Periodic Chemistry Pdf

Periodic chemistry, a fundamental branch of chemistry, deals with the study of the periodic table and its applications in understanding the properties and behavior of elements. The periodic table, a tabular arrangement of the known chemical elements, is organized by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) and are grouped into rows called periods and columns called groups or families.
Introduction to Periodic Chemistry

The periodic table was first developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, and it has undergone numerous revisions since then. The modern periodic table is a powerful tool for chemists, as it allows them to predict the properties and behavior of elements based on their position in the table. The elements in the same group (vertical column) have similar chemical properties, while the elements in the same period (horizontal row) have similar physical properties. The periodic table is a dynamic tool, and new elements are still being discovered and added to the table.
Periodic Trends
One of the key features of the periodic table is the periodic trends, which are the patterns of change in physical and chemical properties that occur as you move across a period or down a group. The main periodic trends are atomic radius, electronegativity, electron affinity, and ionization energy. Atomic radius increases down a group and decreases across a period, while electronegativity increases across a period and decreases down a group. Electron affinity and ionization energy also show similar trends. Understanding these trends is crucial in predicting the properties and behavior of elements.
| Periodic Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Atomic Radius | Increases down a group, decreases across a period |
| Electronegativity | Increases across a period, decreases down a group |
| Electron Affinity | Increases across a period, decreases down a group |
| Ionization Energy | Increases across a period, decreases down a group |

Blocks of the Periodic Table
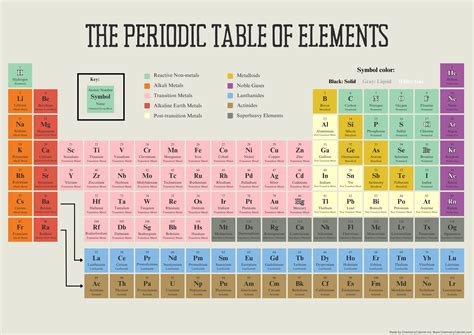
The periodic table can be divided into four blocks: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block. The s-block elements are in the first two groups (alkali metals and alkaline earth metals) and are characterized by their low ionization energy and high reactivity. The p-block elements are in the remaining groups and are characterized by their high ionization energy and low reactivity. The d-block elements are in the middle of the periodic table and are characterized by their ability to form ions with different charges. The f-block elements are at the bottom of the periodic table and are characterized by their high ionization energy and low reactivity.
Group 1 and 2 Elements
Group 1 elements (alkali metals) are highly reactive and have low ionization energy, while group 2 elements (alkaline earth metals) are less reactive and have higher ionization energy. The alkali metals are highly electropositive and tend to lose one electron to form a positive ion, while the alkaline earth metals are less electropositive and tend to lose two electrons to form a positive ion.
Key Points
- The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
- The elements in the same group have similar chemical properties, while the elements in the same period have similar physical properties.
- The periodic trends, such as atomic radius, electronegativity, electron affinity, and ionization energy, are essential in predicting the properties and behavior of elements.
- The s-block elements are highly reactive and have low ionization energy, while the p-block elements are less reactive and have higher ionization energy.
- The d-block elements are characterized by their ability to form ions with different charges, while the f-block elements are characterized by their high ionization energy and low reactivity.
Transition Metals
Transition metals are in the d-block of the periodic table and are characterized by their ability to form ions with different charges. They are highly electropositive and tend to lose one or more electrons to form positive ions. Transition metals are also known for their catalytic properties and are widely used in various industrial applications.
Lanthanides and Actinides
The lanthanides and actinides are in the f-block of the periodic table and are characterized by their high ionization energy and low reactivity. They are highly electropositive and tend to lose one or more electrons to form positive ions. The lanthanides and actinides are also known for their unique magnetic properties and are widely used in various technological applications.
| Block | Description |
|---|---|
| s-block | Elements in the first two groups, characterized by low ionization energy and high reactivity |
| p-block | Elements in the remaining groups, characterized by high ionization energy and low reactivity |
| d-block | Elements in the middle of the periodic table, characterized by ability to form ions with different charges |
| f-block | Elements at the bottom of the periodic table, characterized by high ionization energy and low reactivity |
What is the periodic table, and how is it organized?
+The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number and are grouped into rows called periods and columns called groups or families.
What are the main periodic trends, and how do they relate to the properties of elements?
+The main periodic trends are atomic radius, electronegativity, electron affinity, and ionization energy. These trends are essential in predicting the properties and behavior of elements, as they show patterns of change in physical and chemical properties that occur as you move across a period or down a group.
What are the characteristics of the s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block elements?
+The s-block elements are highly reactive and have low ionization energy, while the p-block elements are less reactive and have higher ionization energy. The d-block elements are characterized by their ability to form ions with different charges, while the f-block elements are characterized by their high ionization energy and low reactivity.
Meta Description: Discover the world of periodic chemistry and learn about the periodic table, periodic trends, and the characteristics of different blocks of elements. Understand how the periodic table is organized and how it can be used to predict the properties and behavior of elements.



