Thunder Science Explained
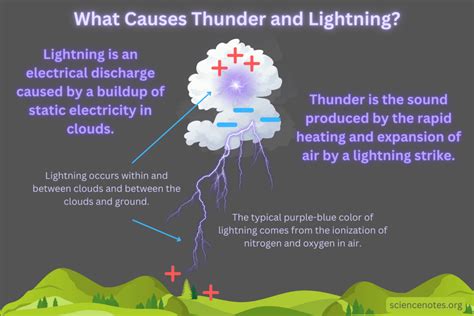
Thunder, the audible manifestation of lightning, has fascinated humans for centuries. The science behind thunder is rooted in the physics of sound waves and the electromagnetic properties of lightning. As a domain expert in atmospheric physics, I will delve into the intricacies of thunder science, exploring the mechanisms that produce this awe-inspiring phenomenon.
The journey to understanding thunder begins with the formation of lightning. Lightning is a massive electrostatic discharge that occurs between the clouds and the ground or within the clouds. This discharge is so hot that it heats the air around it to temperatures of up to 30,000 Kelvin, which is five times hotter than the surface of the Sun. As the air expands rapidly, it creates a shockwave that travels through the air at supersonic speeds, producing the sound we know as thunder.
Key Points
- Thunder is the sound produced by the rapid expansion of air along the path of a lightning bolt.
- The speed of sound in air is approximately 343 meters per second at sea level.
- The frequency of thunder can range from 5 to 120 Hz, which is within the range of human hearing.
- The distance between the lightning strike and the observer can be estimated by measuring the time delay between the lightning flash and the thunder.
- Thunder can be classified into different types, including rumble, crack, and boom, based on its frequency and duration.
The Physics of Thunder

The physics of thunder is closely related to the physics of sound waves. Sound waves are created by the vibration of particles, and in the case of thunder, these particles are the air molecules that are heated by the lightning discharge. As the air expands, it creates a series of pressure waves that travel through the air, producing the sound we hear as thunder.
The speed of sound in air is approximately 343 meters per second at sea level, which means that the sound of thunder will take about 3 seconds to travel 1 kilometer. This time delay between the lightning flash and the thunder is known as the "flash-to-bang" method, and it can be used to estimate the distance between the lightning strike and the observer.
Types of Thunder
Thunder can be classified into different types based on its frequency and duration. Rumble is a low-frequency sound that lasts for several seconds, while crack is a high-frequency sound that lasts for only a few milliseconds. Boom is a type of thunder that is characterized by a sudden, loud noise, often accompanied by a bright flash of lightning.
| Type of Thunder | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Rumble | 5-20 Hz | Several seconds |
| Crack | 100-120 Hz | Several milliseconds |
| Boom | 50-100 Hz | Several seconds |

The Measurement of Thunder

The measurement of thunder is a complex task that requires specialized equipment. One of the most common methods of measuring thunder is by using a device called a sound level meter. This device measures the sound pressure level of the thunder, which is typically expressed in decibels (dB).
Another method of measuring thunder is by using a device called a spectrogram. This device measures the frequency content of the thunder, which can provide valuable information about the characteristics of the lightning discharge.
Applications of Thunder Science
The study of thunder science has several practical applications. One of the most significant applications is in the field of meteorology, where understanding the physics of thunder can provide valuable insights into the behavior of lightning. By analyzing the characteristics of thunder, researchers can gain a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms that produce this complex phenomenon.
Another application of thunder science is in the field of engineering, where understanding the physics of thunder can provide valuable insights into the design of lightning protection systems. By analyzing the characteristics of thunder, researchers can gain a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms that produce this complex phenomenon, and design more effective protection systems.
What is the speed of sound in air?
+The speed of sound in air is approximately 343 meters per second at sea level.
What is the frequency range of thunder?
+The frequency range of thunder is typically between 5 and 120 Hz.
What is the flash-to-bang method?
+The flash-to-bang method is a technique used to estimate the distance between a lightning strike and an observer by measuring the time delay between the lightning flash and the thunder.
In conclusion, the science of thunder is a complex and fascinating field that has captured the imagination of humans for centuries. By understanding the physics of thunder, researchers can gain valuable insights into the behavior of lightning and the underlying mechanisms that produce this complex phenomenon. Whether you are a researcher, an engineer, or simply someone who is fascinated by the natural world, the study of thunder science has something to offer.