Tropical Rainforest Food Web
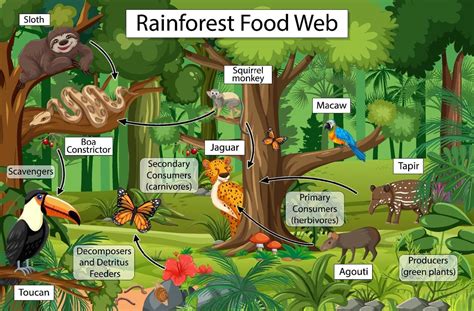
The tropical rainforest is one of the most complex and diverse ecosystems on the planet, with a vast array of plant and animal species interacting and interdependent within a delicate balance. At the heart of this ecosystem is the food web, a intricate network of relationships between predators and prey, where energy and nutrients are transferred from one species to another. In this article, we will delve into the tropical rainforest food web, exploring its key components, relationships, and the crucial role it plays in maintaining the health and biodiversity of this ecosystem.
Key Points
- The tropical rainforest food web is a complex network of relationships between predators and prey, with multiple trophic levels and energy pathways.
- Primary producers, such as plants and algae, form the base of the food web, providing energy and nutrients for herbivores and decomposers.
- Herbivores, such as insects, birds, and mammals, play a crucial role in transferring energy from primary producers to higher trophic levels.
- Predators, such as jaguars, snakes, and eagles, regulate the populations of herbivores and maintain the balance of the ecosystem.
- Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, break down organic matter and recycle nutrients, maintaining the fertility of the soil and supporting the growth of primary producers.
Trophic Levels and Energy Pathways

The tropical rainforest food web is characterized by multiple trophic levels, with energy and nutrients flowing from one level to the next. Primary producers, such as plants and algae, form the base of the food web, converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Herbivores, such as insects, birds, and mammals, feed on primary producers, transferring energy from one trophic level to the next. Omnivores and carnivores, such as jaguars, snakes, and eagles, feed on herbivores and other animals, regulating their populations and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
Primary Producers
Primary producers are the foundation of the tropical rainforest food web, providing energy and nutrients for the entire ecosystem. Plants, such as trees, shrubs, and vines, are the dominant primary producers, using sunlight, water, and nutrients to produce organic compounds through photosynthesis. Algae, such as phytoplankton and cyanobacteria, also play a crucial role in the food web, producing energy and nutrients in aquatic environments.
| Primary Producer | Energy Contribution |
|---|---|
| Trees | 70-80% of total energy |
| Shrubs and vines | 10-20% of total energy |
| Algae | 5-10% of total energy |

Herbivores
Herbivores play a crucial role in the tropical rainforest food web, transferring energy from primary producers to higher trophic levels. Insects, such as beetles, butterflies, and ants, are the most diverse and abundant herbivores, feeding on plants and transferring energy to predators and decomposers. Birds, such as toucans, macaws, and hummingbirds, also feed on plants, fruits, and nectar, while mammals, such as sloths, monkeys, and tapirs, feed on leaves, fruits, and seeds.
Predators and Decomposers

Predators, such as jaguars, snakes, and eagles, play a crucial role in regulating the populations of herbivores and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. These predators feed on herbivores, controlling their populations and preventing any one species from dominating the ecosystem. Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, break down organic matter and recycle nutrients, maintaining the fertility of the soil and supporting the growth of primary producers.
Predator-Prey Relationships
Predator-prey relationships are a critical component of the tropical rainforest food web, with predators regulating the populations of prey species and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. For example, jaguars prey on peccaries, regulating their populations and preventing overgrazing. Similarly, eagles prey on sloths, controlling their populations and maintaining the balance of the forest canopy.
| Predator | Prey | Predator-Prey Relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Jaguar | Peccary | Predation regulates prey population |
| Eagle | Sloth | Predation maintains forest canopy balance |
| Snake | Monkey | Predation regulates prey population and behavior |
Conservation Implications
The tropical rainforest food web is facing numerous threats, including deforestation, habitat fragmentation, and climate change. These threats can disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem, leading to population declines, extinctions, and changes in ecosystem function. Conservation efforts, such as protected areas, sustainable land-use practices, and climate change mitigation, are essential for maintaining the health and biodiversity of the tropical rainforest ecosystem.
What is the role of primary producers in the tropical rainforest food web?
+Primary producers, such as plants and algae, form the base of the food web, providing energy and nutrients for the entire ecosystem.
How do predators regulate the populations of herbivores in the tropical rainforest?
+Predators, such as jaguars, snakes, and eagles, prey on herbivores, controlling their populations and preventing any one species from dominating the ecosystem.
What are the conservation implications of disrupting the tropical rainforest food web?
+Disrupting the tropical rainforest food web can lead to population declines, extinctions, and changes in ecosystem function, highlighting the need for conservation efforts to maintain the health and biodiversity of the ecosystem.
In conclusion, the tropical rainforest food web is a complex and dynamic ecosystem, with multiple trophic levels and energy pathways. Understanding the relationships between predators and prey, primary producers and decomposers, is essential for maintaining the health and biodiversity of this ecosystem. By recognizing the importance of conservation efforts and the need to protect the tropical rainforest ecosystem, we can work towards preserving this unique and valuable ecosystem for future generations.



