What Charge Does A Neutron Have
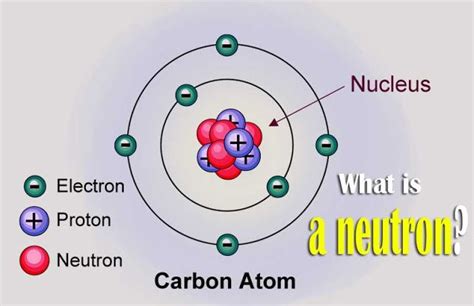
The neutron is a subatomic particle that plays a crucial role in the structure of atomic nuclei. One of the fundamental properties of a neutron is its charge, which is a measure of the amount of electric charge it carries. In the case of neutrons, their charge is precisely zero. This means that neutrons are electrically neutral, neither positively nor negatively charged.
Understanding Neutron Charge

The reason why neutrons have no charge can be understood by looking at their composition. Neutrons are made up of three quarks: two down quarks and one up quark. The down quarks each carry a charge of -1⁄3, while the up quark carries a charge of +2⁄3. When these charges are added together, they cancel each other out, resulting in a net charge of zero for the neutron.
Comparison with Other Subatomic Particles
In contrast to neutrons, protons, which are also found in the nucleus, carry a positive charge of +1. Electrons, which orbit the nucleus, carry a negative charge of -1. The balance between the positive charge of protons and the negative charge of electrons determines the overall charge of an atom, with neutrons contributing to the atom’s mass but not its charge.
| Particle | Charge |
|---|---|
| Proton | +1 |
| Neutron | 0 |
| Electron | -1 |

The fact that neutrons have no charge is fundamental to understanding various phenomena in physics, including nuclear reactions and the structure of matter itself. This property, combined with their mass, makes neutrons an essential component of atomic nuclei, contributing to the nuclear binding energy that holds protons and neutrons together.
Key Points
- Neutrons are electrically neutral, carrying no charge.
- The composition of neutrons, made of two down quarks and one up quark, results in a net charge of zero.
- Neutrons contribute to the mass of an atom but not to its charge.
- The neutrality of neutrons is crucial for the stability of atomic nuclei.
- Understanding neutron charge is fundamental to explaining nuclear reactions and the structure of matter.
Furthermore, the study of neutrons and their properties has led to significant advancements in physics and engineering, including the development of nuclear power and medical treatments. The neutral charge of neutrons allows them to penetrate deep into materials, making them useful for various applications such as neutron scattering experiments, which provide valuable information about the structure and dynamics of materials at the atomic scale.
Applications and Implications

The neutral nature of neutrons also has implications for our understanding of the universe. In astrophysics, neutrons play a key role in the formation of heavy elements in stars and the explosion of supernovae. The study of neutron stars, which are incredibly dense objects composed mostly of neutrons, has provided insights into extreme states of matter and the behavior of gravity under intense conditions.
In conclusion, the charge of a neutron, being precisely zero, is a fundamental aspect of its nature and plays a critical role in the structure and stability of atomic nuclei, as well as in various applications across physics and engineering. Understanding this property is essential for advancing our knowledge of the universe, from the smallest subatomic particles to the vast expanse of cosmic phenomena.
What is the charge of a neutron?
+A neutron has a charge of zero, making it electrically neutral.
Why is the neutrality of neutrons important?
+The neutrality of neutrons is crucial for the stability of atomic nuclei and has significant implications for various applications in physics and engineering.
How do neutrons contribute to the structure of matter?
+Neutrons contribute to the mass of an atom and play a key role in the nuclear binding energy that holds protons and neutrons together in the nucleus.



