What Type Of Macromolecule Is An Enzyme
Enzymes are a type of biological molecule, specifically a class of proteins, that play a crucial role in facilitating and speeding up chemical reactions within living organisms. As proteins, enzymes are considered a type of macromolecule, which is a large molecule composed of many smaller subunits. In the case of enzymes, these subunits are amino acids, which are linked together through peptide bonds to form a long chain or polypeptide.
Classification of Enzymes as Proteins

Enzymes are classified as proteins because they are composed of amino acids and exhibit the characteristic properties of proteins, such as being soluble in water, having a specific three-dimensional structure, and being capable of interacting with other molecules. The unique shape and structure of an enzyme, which is determined by the sequence of amino acids and the interactions between them, allow it to bind to specific substrates and facilitate chemical reactions.
Structure and Function of Enzymes
The structure of an enzyme is critical to its function, as it provides the binding sites for substrates and the catalytic site where the chemical reaction takes place. Enzymes can be composed of a single polypeptide chain or multiple chains, and they can also contain non-protein components, such as cofactors or prosthetic groups, which are essential for their activity. The active site of an enzyme, where the chemical reaction occurs, is typically a small region on the surface of the enzyme that is specifically designed to bind to the substrate and facilitate the reaction.
| Characteristics of Enzymes | Description |
|---|---|
| Composition | Proteins composed of amino acids |
| Structure | Three-dimensional structure with specific binding sites |
| Function | Catalyze chemical reactions by binding to substrates |
| Properties | Soluble in water, specific optimal temperature and pH |

Types of Enzymes and Their Functions
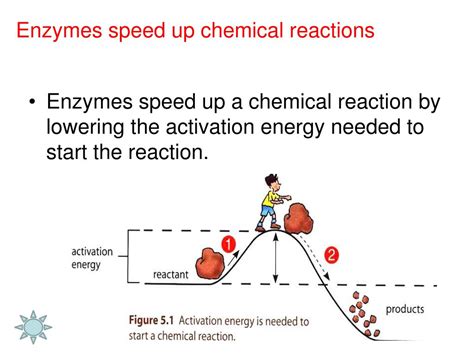
There are six main classes of enzymes, each with distinct functions and characteristics. These classes include oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. Each class of enzyme catalyzes a specific type of chemical reaction, and they play critical roles in various biological processes, such as metabolism, DNA replication, and protein synthesis.
Importance of Enzymes in Biological Systems
Enzymes are essential for life, as they allow cells to carry out the complex chemical reactions necessary for growth, maintenance, and reproduction. Without enzymes, these reactions would occur too slowly or not at all, and life as we know it would not be possible. The study of enzymes has also led to numerous advances in fields such as medicine, where enzymes are used as diagnostic tools and therapeutic agents, and biotechnology, where enzymes are used to develop new products and processes.
Key Points
- Enzymes are a type of protein that facilitates chemical reactions in living organisms
- The structure and function of enzymes are critical to their activity
- Enzymes are classified into six main classes, each with distinct functions and characteristics
- Enzymes play essential roles in various biological processes, including metabolism and DNA replication
- The study of enzymes has led to numerous advances in fields such as medicine and biotechnology
In conclusion, enzymes are a type of macromolecule that plays a critical role in facilitating chemical reactions in living organisms. Their unique structure and properties allow them to bind to specific substrates and facilitate reactions that are essential for life. The study of enzymes has led to numerous advances in various fields, and their importance in biological systems cannot be overstated.
What is the main function of an enzyme?
+The main function of an enzyme is to facilitate and speed up chemical reactions within living organisms by binding to specific substrates and lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
What are the six main classes of enzymes?
+The six main classes of enzymes are oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases, each with distinct functions and characteristics.
Why are enzymes essential for life?
+Enzymes are essential for life because they allow cells to carry out the complex chemical reactions necessary for growth, maintenance, and reproduction. Without enzymes, these reactions would occur too slowly or not at all, and life as we know it would not be possible.



